Google keyword Planner in today’s Digital age is very important to run and optimize your Ad campaign and ensure your budget and bidding strategy matches that of your competitor. In the ever-evolving world of digital marketing, finding the right keywords can make or break your campaigns. Whether you’re focused on search engine optimization (SEO) or pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, keywords are the foundation of your strategy. Enter Google Keyword Planner, a powerful and free tool offered by Google Ads. This tool is indispensable for marketers aiming to identify and utilize the most effective keywords for their business.
What is Google Keyword Planner
Google Keyword Planner is a tool provided by Google Ads that helps you research and find the most relevant keywords for your search campaigns. It provides keyword suggestions, search volume estimates, competition analysis, and cost-per-click (CPC) information. A free tool provided by Google Ads that helps you research and identify the best keywords for your search campaigns. Offering keyword suggestions, search volume data, competition levels, and cost estimates for running PPC campaigns.
Explanation in Simple Words:
In simpler terms, Google Keyword Planner is a free tool from Google that find the best words or phrases to use in your online ads and website content. Therefore, you can see how often certain words are searched on Google and how much competition there is for those words. Hence, This information helps you choose the right keywords to attract more visitors to your website.
Example:
Imagine you own a bakery and want to attract more customers to your website. By using Google Keyword Planner, you can find out how many people are searching for phrases like “fresh bread,” “best cakes,” or “local bakery.” For instance, you might discover that “gluten-free bakery” is a popular search term with moderate competition. Meaning a good number of people are searching for it, but not too many businesses are using it in their ads. You decide to use “gluten-free bakery” in your ad campaign and website content to attract those potential customers. As a result, more people looking for gluten-free options find your bakery online.
How to Set Up Google Keyword Planner ?
Step-by-Step Instructions
1. Set Up a Google Ads Account
First and foremost, to access Google Keyword Planner, you need to set up a Google Ads account. Don’t worry; it’s fast and 100% free.
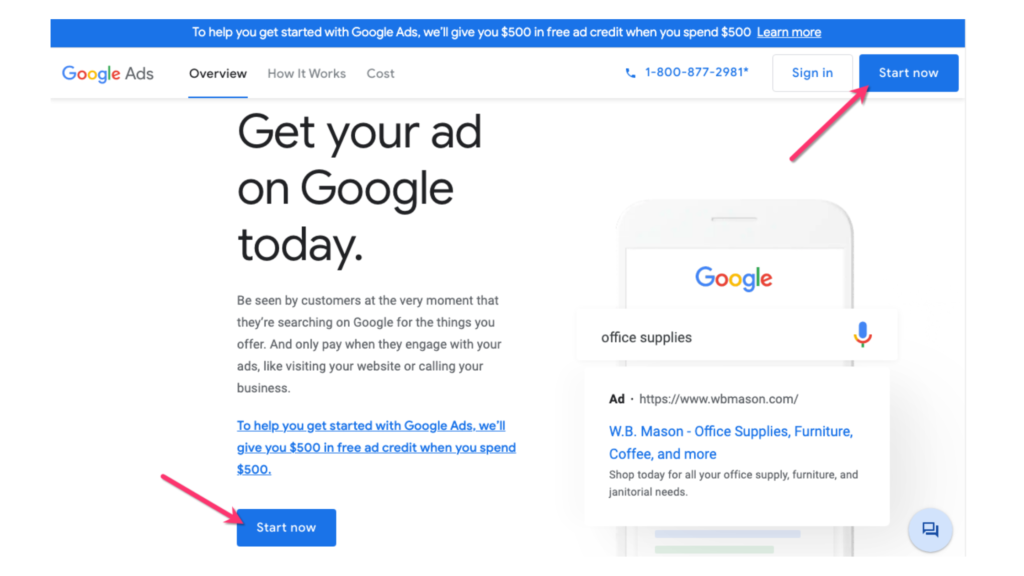
Begin by going to the Google Ads website and clicking on the “Start now” button.
Sign in using your existing Google account, or create a new one if you don’t have an account already.
2. Switch to Expert Mode
Once you’ve signed in, you will see a blue link that says “Switch to Expert Mode.” Click on it. This step is crucial because it allows you to create an account without being forced to create an ad campaign right away.

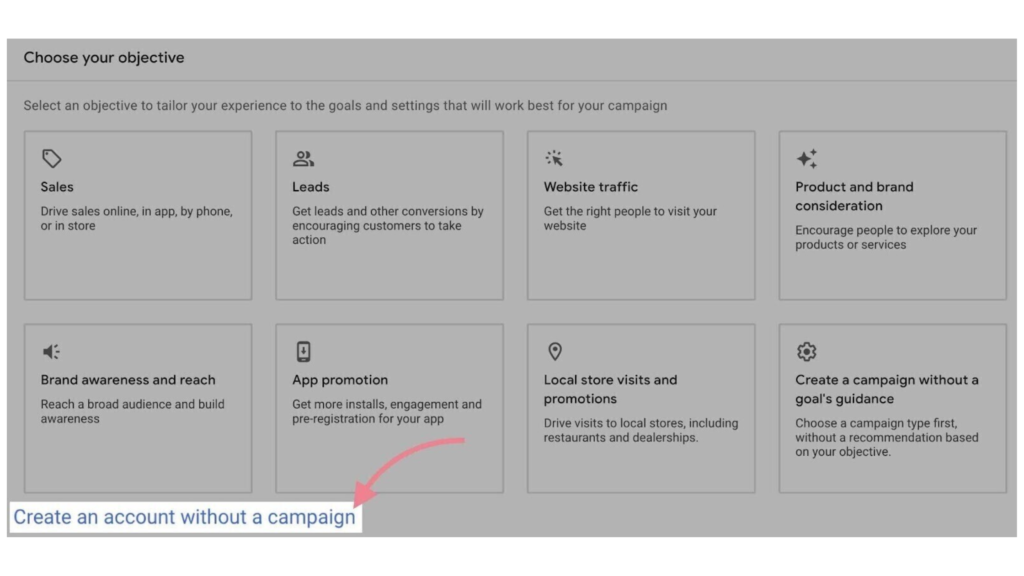
3. Create an Account Without a Campaign
On the next screen, look for the small “Create an account without a campaign” link and click on it. This option helps you bypass the initial ad setup and move directly to the account configuration.
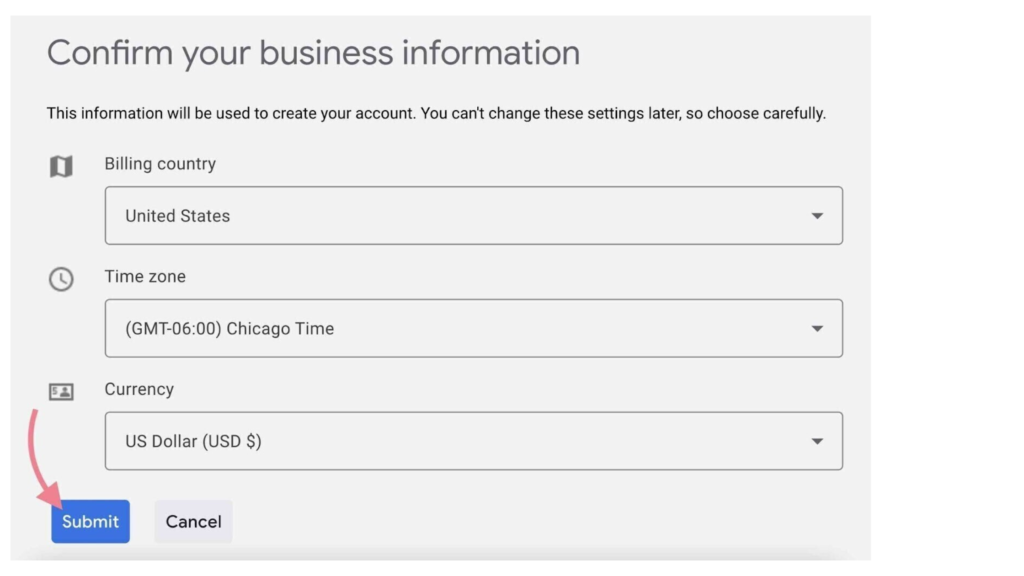
4. Enter Your Account Details
After clicking the link, you will be prompted to select your billing country, time zone, and currency.Fill in these details accurately, and then click the “Submit” button.
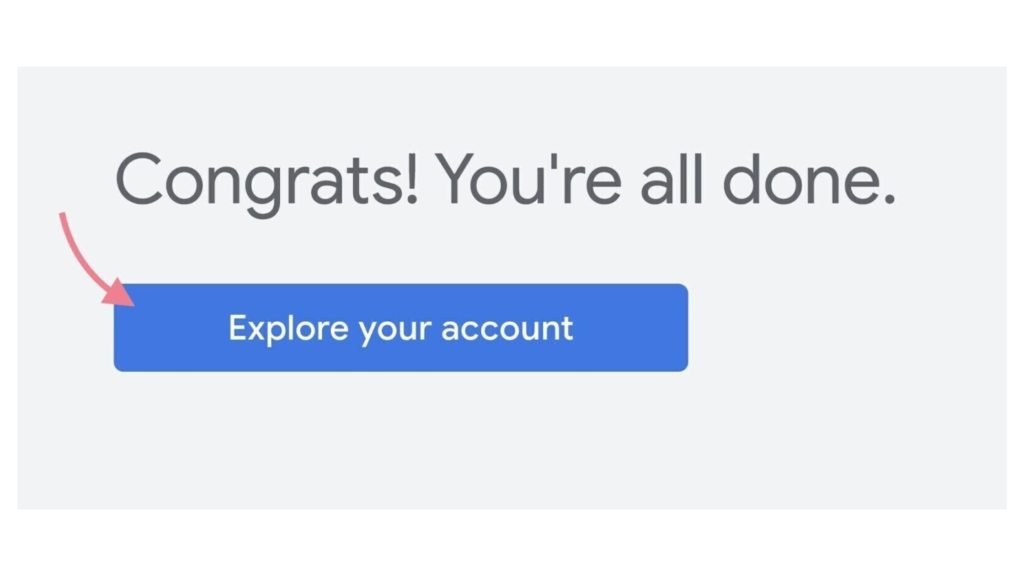
5. Confirm Your Account Setup
Once you’ve submitted your information, you will reach a confirmation page. Here, click on the “Explore your account” button to proceed. Congratulations! Your Google Ads account setup is now complete.
6. Access Keyword Planner
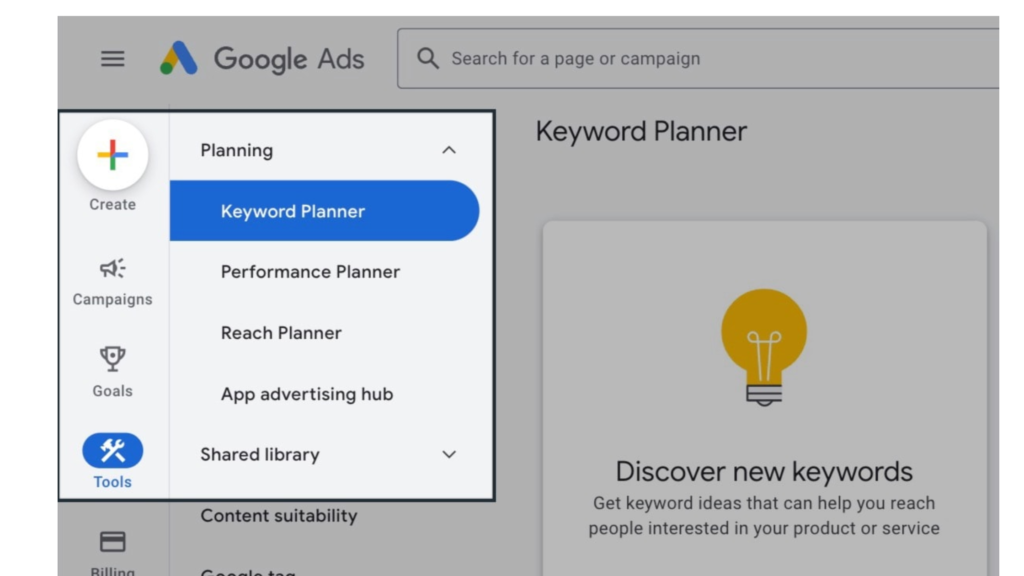
To access the Keyword Planner, go to the menu bar at the top of the page and click on “Tools and settings.”
From the drop-down menu, under the “Planning” column, select “Keyword Planner.”
How to Use Google Keyword Planner Effectively ?
Step-by-Step Instructions
1. Access Google Keyword Planner
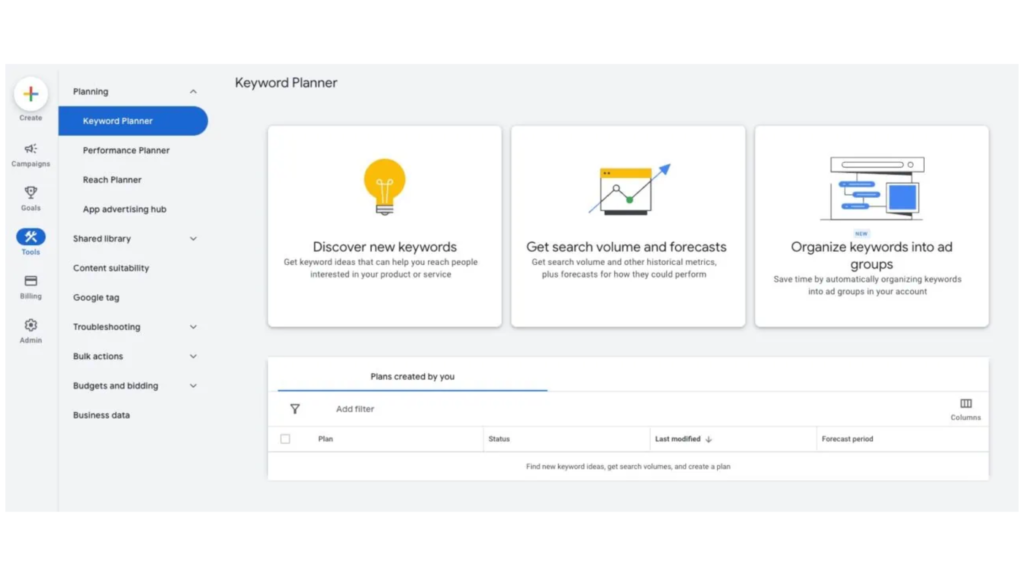
To start, you need to open Google Keyword Planner. Click on “Tools” in the left navigation menu of your Google Ads account. Then, from the drop-down menu, select “Keyword Planner” under the “Planning” column.
You will see three options within Keyword Planner:
- Discover New Keywords
- Get Search Volume and Forecasts
- Organize Keywords into Ad Groups.
2. Choose Your Tool
From the above tools, explore and use the one that suits your campaign goal. Choose “Discover New Keywords” to find new keyword ideas that can help increase your website traffic.
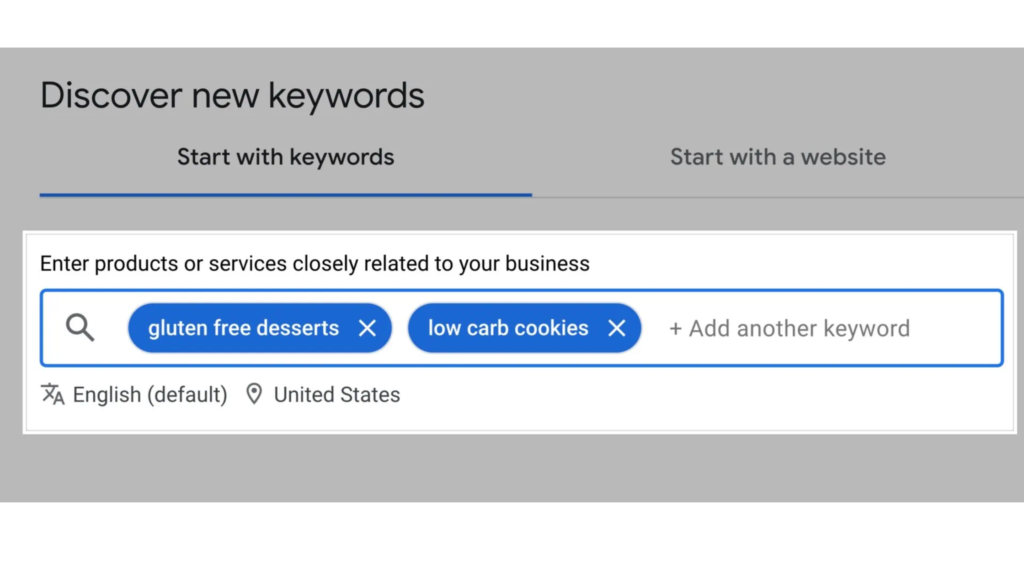
i) Discover New Keywords
Enter products or services closely related to your business into the provided field. This step is crucial because the value you get from the Keyword Planner largely depends on the information you enter.
For example, if you run an eCommerce site that sells cookies, you might enter terms like “gluten-free desserts” and “low carb cookies” here. Be strategic and enter multiple keywords by separating them with commas.
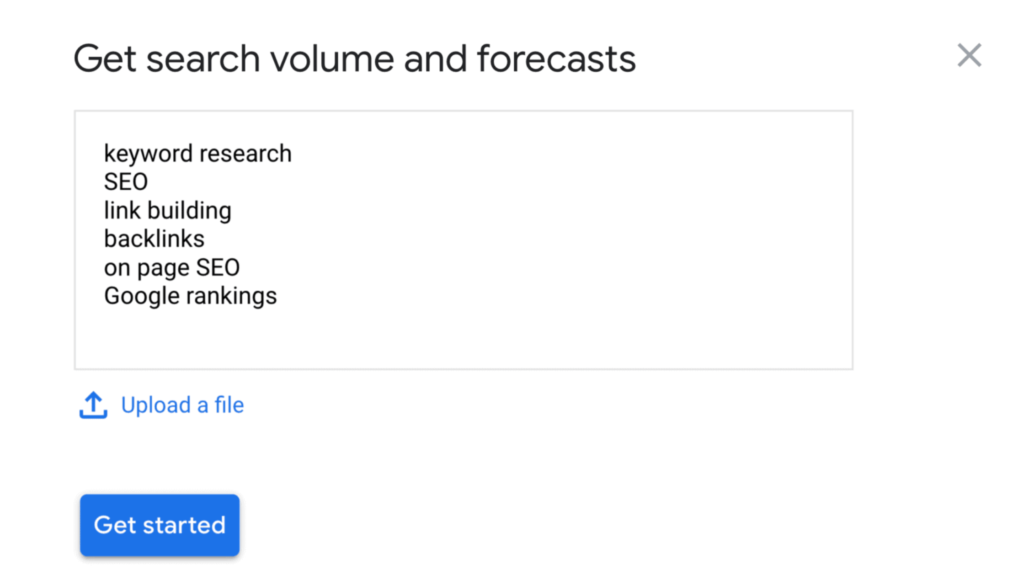
ii) Get Search Volume and Forecasts
If you already have a long list of keywords and want to check their search volume, use this feature.
Copy and paste your list of keywords into the search field and hit “Get Started.” You will see data on the search volume and Google’s predictions on clicks and impressions for the keywords you entered.
iii) Organizing Keywords into ad group
Organizing your keywords in Google Keyword Planner can indeed be a daunting task. However, this process becomes significantly simpler when you use Keyword Planner to help you find the most appropriate placement for new keywords. This organization is based on how your keywords are currently arranged within your relevant campaigns.
When you have a set of new keywords or when you’ve discovered new keyword ideas, Google Keyword Planner can automatically organize these new keywords. The tool identifies and suggests the most relevant ad groups within your campaigns for these keywords.
a) Review and Organize
Once you have your list of new keywords, Keyword Planner will automatically suggest the most suitable ad groups for these keywords based on your existing campaigns. Review these suggestions carefully. You can choose to accept the suggested ad group assignments or manually reassign the keywords to other ad groups if you believe they would perform better elsewhere.
b) Implement the Keywords
After organizing your keywords, you can implement them into your campaigns directly from Keyword Planner. This streamlined process helps to ensure that your keywords are well-placed for optimal performance.
c) Monitor and Adjust
Keep an eye on the performance of your newly added keywords. Monitor key metrics such as click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, and cost-per-click (CPC). Make adjustments as needed to continuously improve the effectiveness of your campaigns.
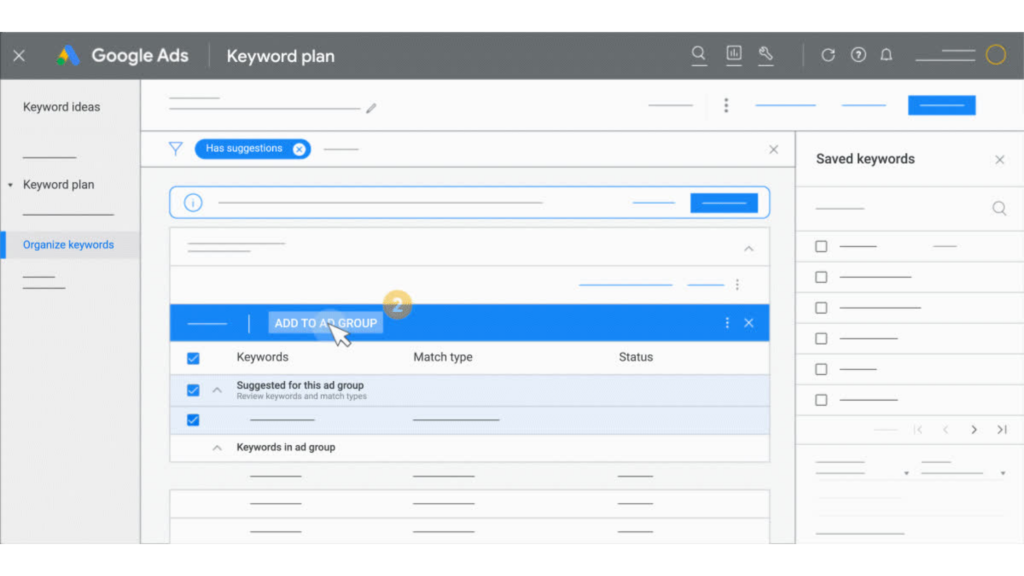
3. Sorting and Filtering
Now it’s time to filter the list of keywords down to a smaller list of terms that are best for you.
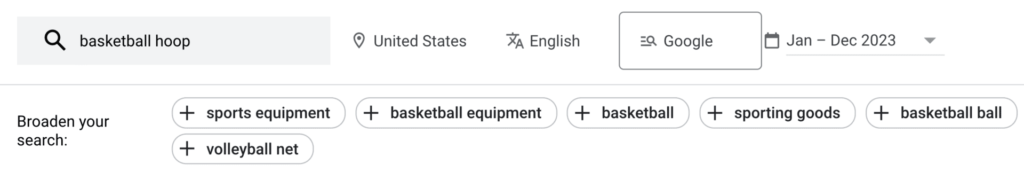
This corner of the page has four terms you can focus on
a) Location
When filtering keyword results, the “Locations” setting is crucial as it specifies the country or countries you are targeting. Transitioning from a general to a more specific audience, this setting ensures your keywords are relevant to the geographic area you want to market to. For instance, if you’re targeting English-speaking people in the United States, you can leave this as the default. However, if your business operates in Germany, it’s essential to change the location to “Germany” and select “German” as the language. This simple but vital step helps tailor your keyword strategy to the right audience, making your campaigns more effective and relevant
b) Language
The “Language” filter in Google Keyword Planner allows you to see information on keywords in a specific language. This feature is automatically set to English if you’re targeting English-speaking people in the United States, but it can be adjusted based on your target audience. For example, if you’re marketing to a German-speaking audience, you would change the language setting to “German.” This adjustment ensures that the keyword suggestions you receive are appropriate and effective for your target demographic, enhancing the overall impact of your SEO and ad campaigns.
c) Search Networks
The “Search Networks” setting determines whether you want to advertise only on Google or on Google and their search partners. Transitioning from general settings, this option is crucial because search partner sites include other search engines and Google properties like YouTube. For most campaigns, it’s recommended to leave this set to just “Google” to maintain focus and precision. This ensures that your ads appear in the primary search network where they are most likely to reach your intended audience effectively.
d) Date Range
The “Date Range” filter allows you to specify the period for which you want to see keyword data. By default, this is set to the past 12 months, which usually provides a comprehensive overview of keyword performance over time. Transitioning from a fixed to a customizable period, this setting can be adjusted based on your specific needs. For example, if you want to analyze seasonal trends, you might choose a shorter date range to capture recent data. Keeping the date range relevant ensures you get the most accurate and useful insights for your keyword planning.
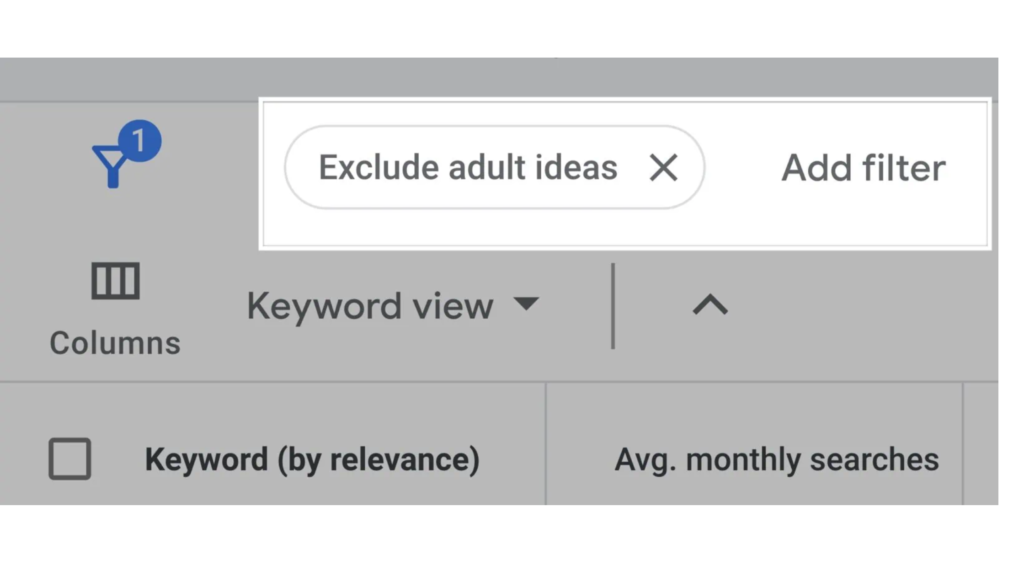
The next part of this step is filtering where you can find ” Add filters “, Let us Break them down one by one
a) Keyword Text
The “Keyword Text” filter allows you to narrow down your results to only include keywords that contain a specific word or phrase. This is particularly useful when you have a specific focus, such as launching a new product line. For example, if you’re introducing a line of blue t-shirts, you would filter to ensure that “blue t-shirt” appears in all suggested keywords. This targeted approach streamlines the process, helping you find the most relevant and strategic keywords for your campaign.
b) Exclude Keywords in My Account
The “Exclude Keywords in My Account” filter helps you avoid redundancy by excluding keywords you’re already bidding on in Google Ads. This feature is beneficial for managing your ad campaigns more efficiently. By transitioning from a broader to a more focused keyword list, it ensures that you’re not overlapping efforts and helps you discover new opportunities without duplicating your current strategy. This way, you can maintain a fresh and effective keyword portfolio.
c) Avg. Monthly Searches
Filtering by “Avg. Monthly Searches” helps you focus on keywords with the right level of search volume. This setting is useful for both avoiding highly competitive keywords and filtering out those with too few searches. For example, if you have a list of keyword ideas, you can sort them by average monthly searches to prioritize terms with substantial search volumes. This ensures that the keywords you target are neither too competitive nor too obscure, optimizing your chances for visibility and engagement.
d) Competition
The “Competition” filter allows you to sort keywords by their competition level, which is determined by how many advertisers are bidding on them in Google Ads. This is distinct from SEO competition and should be used with caution if you’re focusing on organic search. Filtering by “Low,” “Medium,” or “High” competition can help you identify keywords that might be easier to bid on and rank for in paid search. However, it’s essential to remember that this setting is designed for PPC, not SEO, and should be considered accordingly.
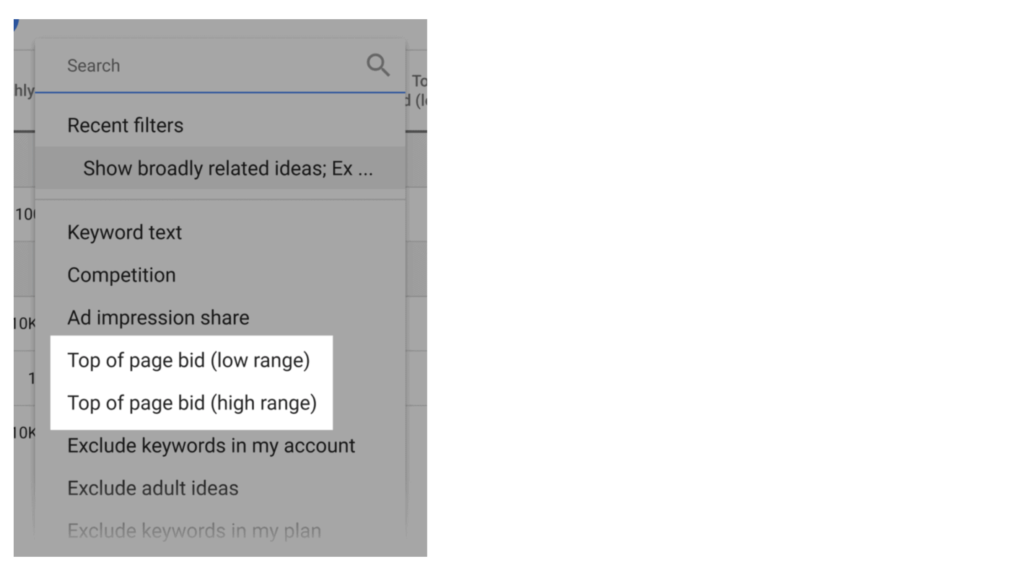
e) Top of Page Bid
The “Top of Page Bid” filter, previously known as “Cost Per Click” (CPC), indicates how much you’d expect to pay for your ad to appear at the top of the search results for a particular keyword. This setting is a proxy for commercial intent, helping you identify keywords that potential buyers are searching for. By setting a range, you can filter out keywords with low commercial intent and focus on those that are likely to convert into sales. This helps in optimizing your ad spend towards more lucrative keywords.
f) Organic Impression Share
The “Organic Impression Share” filter shows how often your site appears in organic search results for a particular keyword. To use this feature, you need to connect your Google Search Console account to Google Ads. This filter is valuable for understanding your organic reach and identifying keywords where you have strong visibility. It helps in refining your SEO strategy by highlighting areas where you are already performing well and where there might be opportunities for improvement.
g) Organic Average Position
The “Organic Average Position” filter indicates where your site ranks on average for each keyword in organic search results. Like the Organic Impression Share, this feature requires a connection between Google Search Console and Google Ads. This setting provides insights into your current organic rankings, helping you identify keywords where you might need to improve your position. By analyzing this data, you can develop strategies to enhance your rankings and increase your organic traffic.
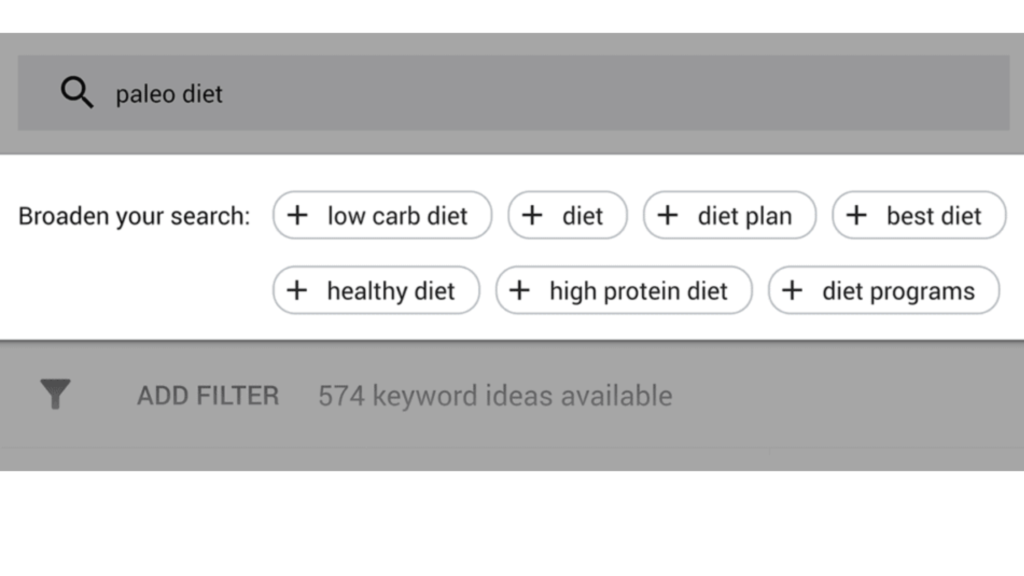
h) Broaden Your Search
The “Broaden Your Search” feature offers suggestions for keywords that are somewhat related to the terms you entered. This new feature is useful for expanding your keyword list with related terms that you might not have initially considered. For example, if you search for “Paleo Diet,” you might receive suggestions like “low-carb diet” or “ketogenic diet.” This helps in discovering additional keywords that can enhance your campaign’s reach and effectiveness.
4. Choose a Keyword
Now that you understand how to use all the tools, features, and options within the Google Keyword Planner, it’s time for the final step: finding the best keywords to optimize your site’s content. This can be tricky because there are many factors to consider, and it’s often more art than science. Here’s a simple guide to help you through this process using an example.
Example
Imagine you run an eCommerce site that sells organic food. You want to write a blog post about the health benefits of organic coffee.
i) Choosing the Right Keyword
Avoid too broad a keyword like “coffee” because it’s too general. Avoid too narrow a keyword like “health benefits of organic coffee” because it’s too specific. A keyword like “organic coffee” is just right.
ii) Using the Tool
Enter “organic coffee” into the Google Keyword Planner and click “Get Started.”
So how do you know which keywords to choose?
When you get a list of keyword suggestions there are many factors you can look at but focus on these three main criteria
a) Search Volume
Look for keywords with high average search volume because they can bring more traffic to your site. More searches mean more potential visitors.
b) Commercial Intent
Check the competition and suggested bid for each keyword. Higher competition and suggested bids usually mean the keyword is valuable and can attract paying customers. Keywords with high commercial intent are more likely to convert visitors into customers.
c) Organic SEO Competition
Evaluate how tough it is to rank for a keyword in organic search results. Look at the websites currently ranking on the first page. The more authoritative and well-established these sites are, the harder it will be to outrank them. Use resources like guides to SEO keyword competition to understand this better.
Now let us cover doubts that many of you readers have about Google Keyword Planner.
1. Is Google Keyword Planner free?
Yes, Google Keyword Planner is free to use, but it offers different levels of features based on whether you have an active Google Ads campaign. With the free version, you can access basic keyword ideas, search volume estimates, and general trends, which are sufficient for basic keyword research and initial planning. However, when you run Google Ads and have an active campaign, you unlock more detailed features. These include precise search volume data, competitive analysis, cost-per-click estimates, and the ability to segment data by various criteria such as location, language, and device. This detailed information helps in crafting more targeted and effective ad campaigns. Essentially, while the free version provides a good starting point, the paid features offer deeper insights and more granular data to enhance your advertising strategies.
2. Can I use Google Keyword Planner without Google Ads account?
No, you cannot use Google Keyword Planner without a Google Ads account. Google Keyword Planner is integrated into the Google Ads platform, making it necessary to have an active Google Ads account to access the tool. This integration is designed to help users create effective advertising campaigns by providing detailed keyword data directly within the advertising interface. Without a Google Ads account, you won’t be able to access the Keyword Planner at all. Google requires users to set up an Ads account to ensure they are using keyword data for creating and optimizing ad campaigns, maintaining a focused and relevant use of their resources.
3. What is the difference between Google Ads Keyword Planner and Google Trends?
Google Ads Keyword Planner and Google Trends are two distinct tools offered by Google, each serving different purposes for keyword research and market analysis. Google Ads Keyword Planner is primarily designed for advertisers who want to create and optimize their ad campaigns. It provides detailed data on search volumes, competition levels, and cost-per-click estimates for specific keywords. For example, if you run an online store selling organic coffee, Keyword Planner can help you identify high-traffic keywords like “organic coffee beans” and estimate how much it would cost to bid on those keywords in a Google Ads campaign.
On the other hand, Google Trends is a broader tool that analyzes the popularity of search queries over time, providing insights into seasonal trends, geographic distribution, and related topics. It is useful for understanding how interest in a particular topic or keyword changes over time and across different regions. For instance, if you want to know when interest in “organic coffee” peaks, Google Trends can show you that searches for this term increase significantly in January and July, which can help in planning your marketing strategy around these periods.
4. Is Google Keyword Planner good for SEO?
Yes, Google Keyword Planner is a valuable tool for SEO, even though it is primarily designed for advertisers. It provides key insights into keyword search volumes, trends, and competition, which are crucial for optimizing content and improving organic search rankings. For instance, if you run a blog about health and wellness and want to write an article on the benefits of meditation, Google Keyword Planner can help you identify relevant keywords like “benefits of meditation,” “meditation for stress relief,” and “how to meditate for beginners.” By understanding the search volume and competition for these keywords, you can strategically incorporate them into your content, making it more likely to rank higher in search engine results.
Moreover, the tool’s data on seasonal trends can help you plan your content calendar. For example, if you notice that searches for “meditation techniques” spike at the beginning of the year, you can time your content to coincide with this increased interest, potentially driving more traffic to your site. While Google Keyword Planner does not provide insights into organic SEO competition as directly as some other SEO tools, its comprehensive keyword data can still form a strong foundation for effective SEO strategies.
5. How much does Google pay per click?
The cost per click (CPC) on Google Ads varies widely depending on factors such as the industry, competition, and keyword relevance. On average, CPC can range from as low as $0.01 to more than $50 per click. For instance, highly competitive industries like insurance and legal services often see higher CPCs. Keywords like “best car insurance” or “personal injury lawyer” can have CPCs exceeding $50 due to intense competition and high commercial intent. Conversely, less competitive industries or niche markets might experience much lower CPCs. For example, a keyword like “local organic farmers market” might only cost a few cents per click. These variations highlight the importance of strategic keyword selection and budget management in a successful Google Ads campaign.
6. How SEO is better than Google Ads?
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) and Google Ads serve different purposes, but SEO often proves to be more beneficial in the long run for several reasons. Firstly, SEO focuses on organic search results, which means that once your website ranks high for certain keywords, you don’t need to pay for each click. This can lead to substantial cost savings over time compared to the pay-per-click model of Google Ads.
For example, if you run a blog about healthy living, investing in SEO to rank high for keywords like “benefits of organic food” can drive consistent, free traffic to your site. In contrast, using Google Ads for the same keywords would require a continuous budget to maintain visibility.
Additionally, organic search results often carry more credibility with users than paid ads. Users are more likely to trust and click on an organic result, believing it to be more authoritative and relevant. This can enhance your brand’s reputation and trustworthiness.
Moreover, SEO can provide lasting benefits. Once you achieve high rankings, maintaining them typically requires less effort compared to the ongoing expense and management of Google Ads campaigns. For example, a well-optimized page for “DIY home improvement tips” can keep attracting visitors long after the initial optimization work is done, while a Google Ads campaign for the same topic would need continuous funding.
7. why do people choose Google Ads and Keyword Planner over SEO?
a) Immediate Results
Google Ads delivers instant visibility and traffic. Once a campaign is launched, ads start appearing in search results, driving immediate traffic to the website. This is particularly beneficial for businesses needing quick results, such as during a product launch or a limited-time promotion.
b) Precise Targeting
Google Ads allows precise targeting of audiences based on location, demographics, interests, and search behavior. This level of specificity helps businesses reach their ideal customers more effectively. For instance, a local bakery can target ads to people searching for “fresh bread near me” within a specific radius.
c) Budget Control
Google Ads offers flexible budgeting options, enabling businesses to control their ad spend and set daily limits. This feature is useful for small businesses with limited marketing budgets, allowing them to compete with larger companies without overspending.
d) Detailed Analytics
Google Ads provides comprehensive performance metrics, allowing businesses to track the effectiveness of their campaigns in real time. Metrics like click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, and cost per acquisition (CPA) help in fine-tuning strategies for better results.
e) Keyword Planner Insights
Keyword Planner is integrated with Google Ads and offers valuable insights into keyword trends, search volumes, and competition levels. This helps businesses identify lucrative keywords for their campaigns. For example, an e-commerce store can discover high-search-volume keywords like “affordable summer dresses” to optimize their ad copy.
f) Competitive Advantage
Google Ads positions ads at the top of search results, often above organic listings. This prime placement can give businesses a competitive edge, especially in highly competitive industries. For example, a new tech gadget company can use ads to appear at the top for searches like “latest tech gadgets” even if their organic ranking is still developing.
g) Consistency and Reliability
SEO can be unpredictable due to algorithm changes and the time it takes to see results. In contrast, Google Ads provides a more predictable and stable approach to maintaining online visibility, making it a safer bet for consistent traffic.
h) Complementary to SEO
Many businesses use Google Ads and Keyword Planner in conjunction with SEO. Ads can drive traffic while waiting for SEO efforts to pay off, and keyword insights can inform SEO strategies. For instance, a company can run Google Ads for immediate visibility while working on improving organic rankings for the same keywords.
To conclude,
In conclusion, understanding the dynamics of Google’s most expensive keywords provides valuable insights into digital advertising strategies across various industries. From legal services commanding CPCs upwards of hundreds of dollars to competitive sectors like finance, insurance, and healthcare, businesses must navigate a landscape where the cost per click reflects both the potential return on investment and the intense competition for valuable leads. Effective keyword management and strategic bidding are essential for maximizing advertising budgets and achieving campaign objectives. By focusing on high-value keywords tailored to specific business goals, organizations can optimize their Google Ads campaigns to attract qualified traffic and ultimately drive conversions in a competitive digital marketplace.
Yashika N Choudhary | Intern Digital Marketer at Inspyr
